Studies Archive
Behavioral Health Treatment Shifts Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic
April 2, 2023Key Takeaways
-
Between 2019 and 2022, there was almost no change in the proportion of patients diagnosed with either anxiety or depression who did not receive treatment. A higher proportion of patients are treated with psychotherapy alone, absent medication management.
-
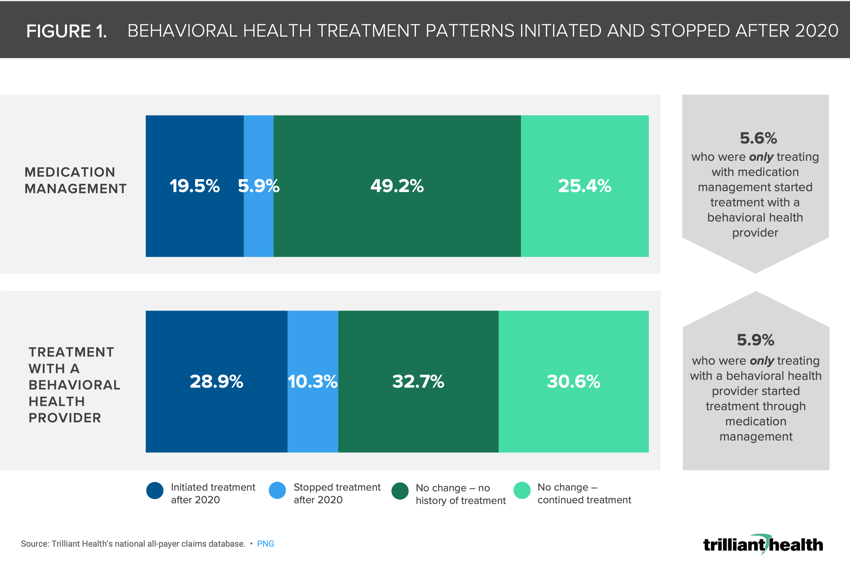
After 2020, 28.9% of patients diagnosed with a behavioral health condition as of 2018 newly initiated treatment with a behavioral health provider and 19.5% of patients newly initiated medication management.
-
Just 5.9% of patients diagnosed with a behavioral health condition as of 2018 stopped treatment via medication management and 10.3% of patients that previously treated with a behavioral health provider stopped receiving treatment after 2020.
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed when, where, why and how Americans access healthcare services. Between January 2018 and December 2019, 96% of adults had at least one encounter with the healthcare system. Among that population, only 89% had returned to receiving healthcare services as of 2021, and only 43% had returned solely to care that is unrelated to COVID-19.1
Background
Past analyses of routine evaluation and management (E&M) visits have revealed that average monthly patient volumes in 2021 were lower than 2018 levels in 79% of metropolitan areas.2 Even though Americans have resumed other activities like travel and in-person work, patients are not returning to routine care. On average, national patient volume was 11.2% lower from 2019 to 2021. But how did approaches to behavioral health treatment change in the face of the pandemic?
In contrast with E&M visits, patient and visit volumes for behavioral health services have steadily increased since the onset of COVID-19. Our 2023 Behavioral Health Trends Report revealed how more anxiety and depression patients were receiving psychotherapy in the wake of the pandemic. Between 2019 and 2022, there was almost no change in the proportion of patients diagnosed with either anxiety or depression who did not receive treatment. A higher proportion of patients are treated with psychotherapy alone, absent medication management.
To expand our understanding of behavioral health treatment changes amid the pandemic, we expanded this analysis and examined a broader set of conditions. For patients diagnosed with any behavioral health diagnosis as of 2018, what share of patients stopped treatment, started treatment or did not experience any change in care due to COVID-19?
Analytic Approach
To understand treatment patterns for behavioral health patients, we identified patients who were diagnosed with any behavioral health condition as of 2018. Among patients with a diagnosed behavioral health condition, medical and pharmacy claims were used to examine treatment through medication management or through engaging with a behavioral health provider. We limited our analysis to patients who were continuously enrolled in a health plan between 2018 and 2022. Of those patients, changes in treatment (i.e., initiating or ceasing provider-based care and prescription medication management) after 2020 were analyzed.
Findings
After 2020, 28.9% of patients diagnosed with a behavioral health condition as of 2018 newly initiated treatment with a behavioral health provider and 19.5% of patients newly initiated medication management (Figure 1). Just 5.9% of patients ceased medication management treatment, while 10.3% of patients previously treated by a behavioral health provider stopped receiving treatment after 2020.
Additionally, 5.9% of patients that previously were receiving treatment with a behavioral health provider began supplementing their treatment with medication management. Alternatively, 5.6% of patients that previously were only using medication management initiated treatment with a behavioral health provider.
The pandemic impacted access to and utilization of healthcare services. In some ways, the barriers to access healthcare increased—especially for patients with previously established behavioral health care (e.g., in-person psychotherapy)—while other historical barriers were reduced or eliminated, such as telehealth and telehealth prescribing.
Thanks to Katie Patton for her research support.
Dive deeper into the findings with Service Line Intelligence | Behavioral Health, a premium subscription that analyzes changes in Behavioral Health demand, supply and yield at the condition, therapeutic, provider and market levels.











.png)

















.png?width=171&height=239&name=2025%20Trends%20Report%20Nav%20(1).png)